Dementia and reducing your risk
The Australian Government has released the National Dementia Action Plan, a joint initiative between the Australian Government and state and territory governments, and you are invited to provide your feedback. It is a 10 year plan that will put people living with dementia, their families, and carers at the centre of all action on dementia and the vision where Australians understand dementia, people living with dementia and their carers have the best quality of life possible and no one walks the dementia journey alone.
You can provide your feedback here, before the 31st January 2023.
Aligning with the release of the National Dementia Action Plan, we look at dementia and the important ways you can reduce your own risk.
What is Dementia?
Dementia is a term used to describe the decline in mental abilities that can affect memory, thinking, language, judgment, and behaviour. It’s an umbrella term for a group of diseases that cause progressive loss of brain function. While there’s no cure for dementia yet, it’s possible to reduce your risk of developing this condition by making lifestyle changes and seeking early diagnosis if you have any concerns about your cognitive health.
However, people often lead active and fulfilling lives for many years after their diagnosis.
Signs and symptoms
Early signs of dementia can be subtle and may not be immediately obvious and its important to note that no two people experience dementia in the same way. However, it is essential to get a medical diagnosis when symptoms first appear, so knowing these common symptoms is very important:
- memory loss
- changes in planning and problem-solving abilities
- difficulty completing everyday tasks
- confusion about time or place
- trouble understanding what we see (objects, people) and distances, depth and space in our surroundings
- difficulty with speech, writing or comprehension
- misplacing things and losing the ability to retrace steps
- decreased or poor judgement
- withdrawal from work or social activities
- changes in mood and personality.
Risk reduction
There are some important things you can do to reduce the risk of dementia. The most important step in reducing the risk of developing dementia is to focus on overall health and wellness. This includes:
Healthy diet
Eating a balanced and healthy diet that focuses on nutrients such as antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins can help protect cognitive health. Eating food rich in antioxidants such as fruits, vegetables, nuts and whole grains may reduce inflammation caused by free radicals which can damage cells over time. Additionally, increasing intake of omega-3 fatty acids can have a positive effect on brain function and slow down age-related memory decline. Foods like salmon, tuna, walnuts, chia seeds and flaxseeds are all good sources of Omega-3s.
Physical activity
Physical activity is also important for brain health. Moderate aerobic exercise can help by promoting the formation of new connections between nerves and increasing blood flow to the brain.
Active mind
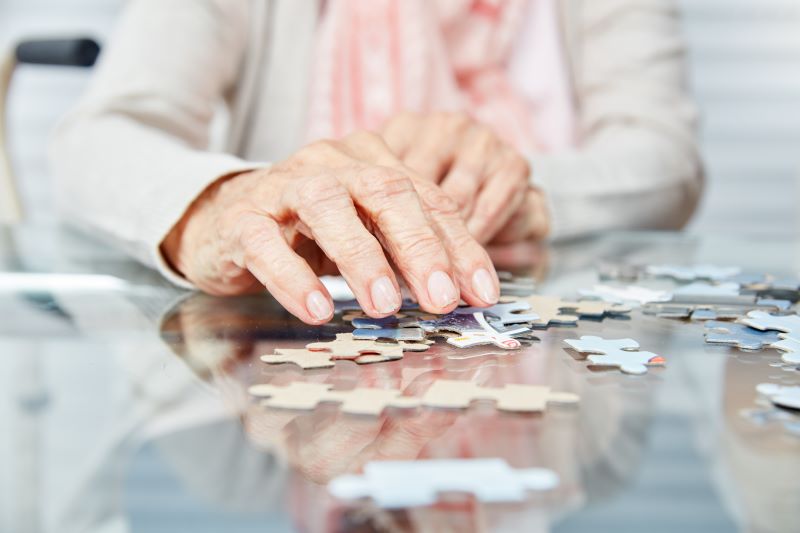
An active mind can be key to delaying the onset of dementia. Activities such as reading, writing and playing games all challenge and keep your brain active, which is beneficial for your brain health. Some activities you can try include learning new skills, playing games, jigsaw puzzles, word and number puzzles, playing an instrument and participating in a creative hobby.
Lifestyle
Other lifestyle activities that promote cognitive health include managing stress levels effectively, limiting alcohol and sugar consumption, not smoking, and getting enough sleep every night. Participating in activities that you enjoy, has also been found to improve cognitive health, such as spending time in nature, spending time with friends and participating in hobbies.
Early Diagnosis
An early diagnosis is also key when it comes to treating dementia. Early detection allows for more effective treatment options including lifestyle changes, medications and therapies that may slow down or prevent further decline. An early diagnosis is usually done through assessment tools such as memory tests or neurological evaluations. These assessments allow doctors to determine if there’s cause for concern and if further investigation is needed.
By making lifestyle changes, paying attention to cognitive health and seeking early diagnosis, if necessary, you can reduce your risk of developing dementia and improve overall well-being. It’s important to remember that dementia is not an inevitable part of aging and seeking advice from your doctor about symptoms such as memory loss, confusion or personality changes can help get the right treatment sooner.
With these tips in mind, we hope this information has been helpful as you take steps towards bettering your physical and mental health!
Interested in similar articles? Why not check these out:
Sources: